The Budget 2023 maintains its incremental approach to addressing India’s economic challenges, along with some bold and transformative steps. The Union Budget of India is a crucial document that outlines the government’s economic and financial plan for the country for the coming fiscal year. Since it has significant ramifications for the Indian economy and people’s lives, it is closely studied by economists, corporations, and residents alike. The finance minister introduced the Union Budget 2023, which addressed some of the most important issues confronting the nation, including recovering growth, increasing jobs, and ensuring financial stability. In this blog, we will examine the How budget is prepared, its objectives, and Budget 2023 highlights.
When is the Budget Presented?
- Union Budget is presented every year on 1st February
Who Presents the Budget?
- Union Budget is presented by Union Finance Minister with the prior recommendation of the President of India.
What is the Budget process?
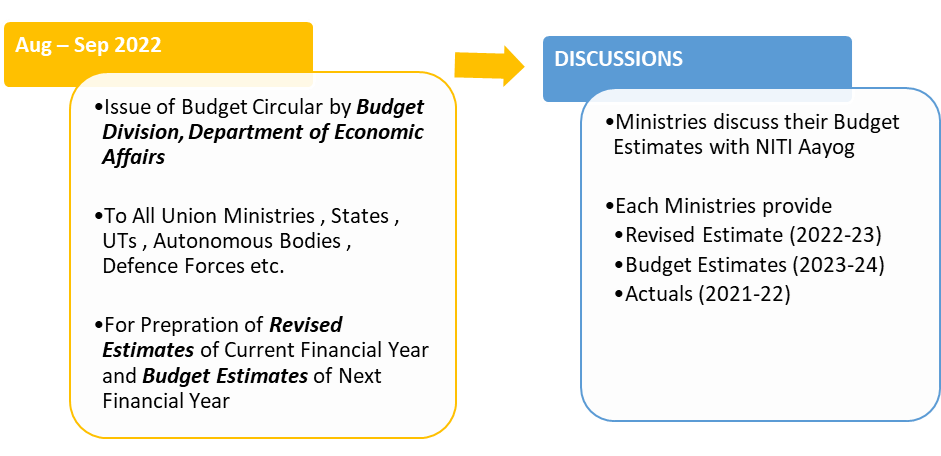
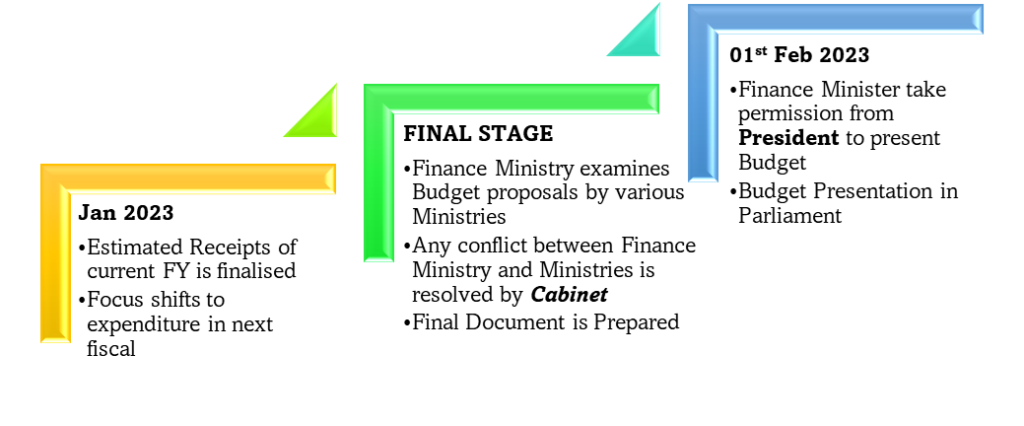
What are the documents in Budget Presentation?
The list of Budget documents presented to Parliament besides the Finance Minister’s Budget Speech is given below:
- Annual Financial Statement (AFS): Article 112
- Demands for Grants (DG): Article 113
- Finance Bill: Article 110(a)
- Fiscal Policy Statements mandated under FRBM Act (Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act,2003):
- Macro-Economic Framework Statement
- Medium-Term Fiscal Policy cum Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement
- Expenditure Budget
- Receipt Budget
- Expenditure Profile
- Budget at a Glance
- Memorandum Explaining the Provisions in the Finance Bill
- Output Outcome Monitoring Framework
- Key Features of Budget 2023 – 24
- Implementation of Budget Announcements: 2022-23
Other documents at Serial Nos. E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are in nature explanatory statements supporting mandated documents with narrative in a user-friendly format suited for quick or contextual references.
The “Output Outcome Monitoring Framework” will have clearly defined outputs and outcomes for various Central Sector Schemes and Centrally Sponsored Schemes with measurable indicators against them and specific targets for FY 2023-24.
What are Budget 2023 Objectives?
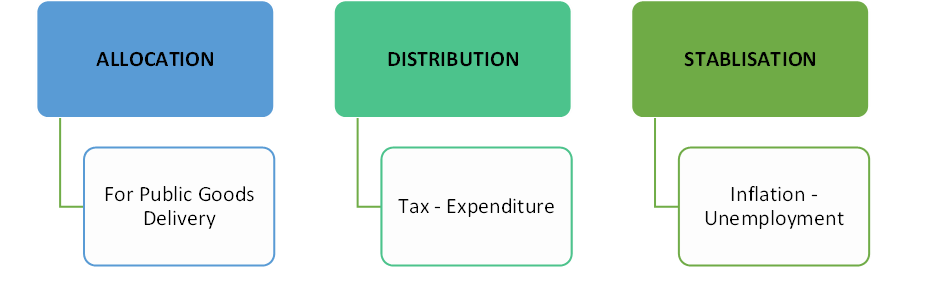
ALLOCATION of Budget – For Public Goods Delivery
- E.g. Defence, Roads, etc
- Benefits to all
- No rival relations
- Free Rider Problem: difficult to exclude anyone
DISTRIBUTION of Budget
- Tax – Expenditure Balance
- Fair
- Subsidies
- Affects Personal Disposable Income [PDI]
- PDI [Personal Income – Tax] = Basic Needs + Consumer Goods + Savings + Investment
STABILISATION
- [ECONOMIC GROWTH] INFLATION – UNEMPLOYMENT Balance
- The level of Aggregate Demand depends upon
- Income
- Credit Availability
- The balance between OUTPUT (Supply) – DEMAND
Vision For Amrit Kaal –
1] Opportunities for citizens with a focus on youth
2] Growth in job creation
3] Strong and Stable Macro-Economic Environment
Priorities of Union Budget 2023
Key Points & Budget 2023 Highlights
As per the thought ‘Saptarishi’ is guiding us through the Amrit Kaal. They are as follows:
1) Inclusive Development: The Government’s slogan of Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas has been a main point for inclusive development
2) Reaching the Last Mile: In the budget, while announcing the ‘Saptarishi’ points the Finance Minister said that Prime Minister Vajpayee’s government had formed the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Department of Development of North-Eastern Region to provide a sharper focus to the objective of ‘reaching the last mile’.
3) Infrastructure and Investment: Digital Public infrastructure for agriculture will be built as an open source, open standard, and interoperable public good – said Nirmala Sitharaman, Finance Minister.
She also said that the Government will launch an Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme to increase the availability of disease-free, quality planting material for high-value horticultural crops.
4) Unleashing the Potential – Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that to enhance the ease of doing business, more than 39,000 compliances have been reduced as well as more than 3,400 legal provisions have been decriminalized.
5) Green Growth: The Finance Minister said that the PM has given a vision for “LiFE” which means Lifestyle for Environment, for a movement toward an environmentally conscious lifestyle. India is firmly moving forward for the ‘Panchamrit’ and net-zero carbon emission by 2070 to usher in a green industrial and economic transition.
6) Youth Power: Smt. Sitharaman said that to empower the youth and help the ‘Amrit Peedhi’ realize their dreams, the Government has created the National Education Policy, focussing on skills, adopted economic policies that facilitate job creation at scale, and that support business opportunity.
7) Financial Sector: Smt. Sitharaman said that last year, She had proposed the credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs and announced happily that the revamped scheme will take effect from 1st April 2023 through the infusion of Rs 9,000 crore in the corpus.
The Finance Minister added that a “National Financial Information Registry” will be set up for serving as the central repository of financial and ancillary info. A new legislative framework will govern this credit public infrastructure, and it will be designed in consultation with the RBI [Reserve Bank of India]
Note:
We have uploaded the infographic of the Union Budget 2023 with the Key Budget Highlights on our Instagram page
Subscribe to CIVILS IAS Youtube Channel for more interesting videos
Get more information on CIVILS IAS Courses or connect with us at any of our branch in Delhi, Ahmedabad or Vadodara.

